Are you tired of remembering to take a pill every day or worried about the effectiveness of other birth control methods? It’s time to consider an intrauterine device (IUD). This small, T-shaped device is inserted into the uterus and can provide up to 10 years of highly effective contraception. Yet, choosing the best IUD Birth control for you can be difficult given the variety of IUDs on the market.
For this reason, we’ve put up this thorough IUD birth control guide, which goes over all you need to know about this well-liked contraceptive option. We’ll discuss the pros and cons of IUDs, the different types available, and what to expect during and after insertion. You will have all the information you need to decide whether an IUD is the best option for you at the end of this guide.
What Are IUDs?
In order to prevent pregnancy, intrauterine devices, often known as IUDs, are implanted into the uterus. They are a type of long-acting reversible contraception. They are small, T-shaped devices made of plastic or copper that are placed inside the uterus by a healthcare provider. IUDs function by delaying or obstructing the ability of a fertilized egg to implant in the uterus.
Types Of IUDs (Intrauterine device)
- Hormonal IUD Birth control is a popular option for many individuals due to its ability to reduce menstrual bleeding and cramping. There are currently four types of hormonal IUDs available on the market: Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta, and Skyla. Mirena and Liletta can provide up to 5 years of protection, while Kyleena and Skyla can last for up to 3 years. The progestin that is released into the uterus daily by hormonal IUDs thins the lining of the uterus and thickens the cervical mucus.
This makes it harder for the sperm to fertilize the egg and decreases the likelihood that a fertilized egg will implant in the uterus. Menstrual cycles can be regulated, period cramps can be less painful, and hormonal IUDs can even be used to treat disorders like endometriosis. With hormonal IUDs, some people may experience side effects including headaches, acne, or mood swings, although these side effects are often minimal and usually go away after a few months. To decide if a hormonal IUD is the best option for you, it’s crucial to discuss any worries or inquiries you may have with your healthcare professional. - The copper used to make non-hormonal IUD birth control is poisonous to sperm and causes an inflammatory reaction in the uterus, which prevents conception. Copper IUDs are highly effective at preventing pregnancy and can stay in place for up to 10 years. These are a great alternative for those who must avoid hormonal birth control owing to health issues or who prefer a non-hormonal type of birth control. As copper IUDs don’t contain hormones, they don’t result in hormonal side effects including acne, weight gain, or changes in mood. However, for some people, particularly in the first few months following insertion, they can result in increased menstrual bleeding and cramps. It’s crucial to remember that copper IUDs do not offer STD protection, so using condoms in addition to an IUD is advised to lower the risk of contracting a STI. Overall, copper IUDs are a highly effective, long-term, non-hormonal contraceptive option for people who want reliable birth control without the use of hormones.
Mirena And Paragard Contraception
Mirena and Paragard are two popular types of IUD birth control that work differently to prevent pregnancy. Mirena is a hormonal IUD that releases a progestin hormone called levonorgestrel. This hormone thickens the cervical mucus, which makes it more difficult for sperm to reach the egg. Additionally, the hormone thins the lining of the uterus, which makes it less likely for a fertilized egg to implant. Mirena is effective for up to 7 years and is often preferred by people who experience heavy or painful periods, as it can decrease bleeding and cramping.
On the other hand, Paragard is a non-hormonal IUD that is made of copper. Copper is toxic to sperm, which prevents fertilization. Paragard is effective for up to 10 years and is often preferred by people who do not want to use hormonal birth control or who experience few side effects from copper. Both Mirena and Paragard are safe and effective forms of birth control, and the choice between them depends on individual preferences and medical history. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider to determine which type of IUD is right for you.
The Pros of IUD Birth Control
There are many benefits to using an IUD birth control for birth control. Firstly, IUDs are highly effective, with a failure rate of less than 1%, making them one of the most reliable forms of birth control available. They are also a long-term contraceptive option, lasting between 3-10 years depending on the type, which means you don’t have to worry about daily maintenance or frequent doctor’s visits. IUDs are also very convenient since they can be inserted at any time during the menstrual cycle, making them a great option for people who may have difficulty remembering to take a pill every day. Additionally, IUDs are a reversible form of contraception, meaning that fertility returns quickly after removal, allowing for a swift return to trying to conceive. Another benefit of using an IUD is that they are suitable for people who cannot use hormonal contraceptives due to medical reasons or personal preference, since there are both hormonal and non-hormonal IUDs available. Hormonal IUDs can also be an effective treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding, endometriosis, and other menstrual-related conditions. Overall, using an IUD for birth control provides many benefits, including high effectiveness, long-term protection, convenience, reversibility, and suitability for a wide range of individuals.
It Can Be Used While Breastfeeding: Some women may choose to use this form of contraception while breastfeeding; however there is not enough research available on whether this is safe or not so please consult with your doctor before making any decisions regarding breastfeeding while using an IUD method.* Reduced Cramping and Bleeding: Many women who have previously had problems with cramps during their period find that their symptoms improve once they start using an intrauterine device because they don’t have periods anymore due to its long-term effectiveness.*
The Cons of IUD Birth Control
While IUD birth control is a safe and effective form of birth control, it may not be the best option for everyone. One of the main cons of using an IUD is that it can cause side effects.
- MILD TO MODERATE CRAMPS AND SPOTTING: Some people may find hormonal side effects including mood swings, weight gain, or acne annoying, such as those brought on by hormonal IUDs. Increased menstrual bleeding and cramping are possible side effects of non-hormonal copper IUDs. If you do experience discomfort during insertion, we can prescribe medication to help manage it (the same goes if you have severe pain during your period).

- PERIODS MAY BECOME HEAVIER AND LONGER: With an IUD in place, you’ll likely get your period more often than before–sometimes as frequently as every month! This can be especially annoying if you’re used to getting fewer periods overall or having them spaced out further apart than every 28 days.
- IRREGULAR BLEEDING: Some women’s periods become irregular after getting an IUD because their bodies haven’t adjusted yet (and this will likely happen regardless of whether or not there was any bleeding before placement). However, many other women report consistent bleeding patterns after being fitted with an intrauterine device (IUD), so keep an eye out for changes in how often or how heavy your flow is each month.*
- INCREASED RISK OF INFECTION: Since the cervix sits just outside of where these devices are placed, there’s an increased risk of infection occurring due to contact between these areas throughout intercourse and other sexual activities. It’s important to note that while IUDs are highly effective at preventing pregnancy, they do not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Therefore, it’s recommended to use condoms in addition to an IUD to reduce the risk of STIs.
- PERFORATION OF THE UTERUS: Additionally, there is a small risk of perforation, or the IUD puncturing the uterine wall, during insertion or removal. While this is rare, it can cause serious complications and may require surgery to remove the IUD. In some cases, an IUD may also be expelled from the uterus, meaning it falls out on its own. This is more common in the first few months after insertion, and if it occurs, the IUD is no longer effective at preventing pregnancy. Lastly, while IUDs are a safe and effective form of birth control, it’s important to consider the potential side effects and risks before deciding if an IUD is the right option for you.
Who Should Use An IUD?
IUD birth control is an excellent option for many individuals who are looking for a reliable, long-term form of birth control. They are safe, highly effective, and can stay in place for several years without needing to be replaced. IUDs are a good option for people who may not want or remember to take a daily pill or use other forms of birth control consistently, such as condoms or vaginal rings. They are also a good option for individuals who cannot use hormonal birth control due to medical reasons, such as a history of blood clots or breast cancer.
Furthermore, IUDs are a good option for people who want to start a family in the future, as they can be removed at any time, and fertility usually returns immediately. This makes IUDs a more convenient option for people who may be considering having children in the next few years. Additionally, IUDs are an excellent option for people who are breastfeeding, as they do not contain hormones that can affect milk supply.
Moreover, IUDs are a good option for people who have had multiple sexual partners or who are at higher risk for sexually transmitted infections (STIs), as they can be used in combination with condoms to provide dual protection. For individuals who are in monogamous relationships and are at lower risk for STIs, a hormonal IUD may be the best option as it provides long-term pregnancy protection with fewer side effects.
Overall, IUDs are a good option for many individuals who are looking for a long-term, highly effective form of birth control. However, it’s important to talk to a healthcare provider to determine if an IUD is the best option for your individual needs, lifestyle, and medical history. Your healthcare provider can help you choose the right type of IUD and answer any questions you may have about the benefits and risks of this popular form of birth control.
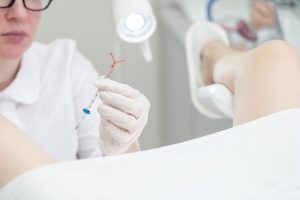
What to Expect During IUD Insertion
If you’re considering getting an IUD birth control, it’s important to be aware of what to expect during the insertion process. Here are some things to consider:
- Timing: IUDs can be inserted at any time during your menstrual cycle, but it’s best to schedule the appointment when you’re not on your period. This can make the insertion process more comfortable and reduce the risk of infection.
- Pain management: While everyone experiences pain differently, IUD insertion can be uncomfortable or even painful for some people. Your healthcare provider may recommend taking an over-the-counter pain reliever, such as ibuprofen, before the procedure to help manage any discomfort.
- Preparing for insertion: Your healthcare provider will explain the insertion process and what to expect. You may need to undress from the waist down and lie on an exam table. They will then insert a speculum into your vagina to hold it open and clean the area with an antiseptic solution.
- The insertion process: The IUD will be inserted into your uterus using a small tube or applicator. Some people experience cramping or discomfort during insertion, while others may not feel anything at all. The entire process typically takes only a few minutes.
- Aftercare: After the IUD is inserted, your healthcare provider may recommend resting for a few minutes before getting up. It’s common to experience cramping or mild discomfort for a few days after insertion, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers. You should also avoid tampons, intercourse, and swimming for a few days after insertion to reduce the risk of infection.
IUD Inserted: Tips for Managing Side Effects
- While IUDs are a highly effective form of birth control, they can cause some side effects, especially in the first few months after insertion. Fortunately, there are several tips you can follow to manage these side effects and make the transition to using an IUD as smooth as possible.
- Pain Relief: One of the most common side effects of IUD birth control insertion is cramping and discomfort. Taking over-the-counter pain relief medication such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help to manage this discomfort. Applying a heating pad to your lower abdomen can also help to soothe cramps.
- Expect Changes in Your Menstrual Cycle: Hormonal IUDs may cause changes in your menstrual cycle, such as irregular bleeding, spotting or longer periods. Copper IUDs may cause heavier bleeding and cramping. These changes are usually temporary and may lessen over time. In the meantime, wearing panty liners or light pads can help you feel more comfortable.
- Keep an Eye on Your Strings: After your IUD is inserted, your healthcare provider will show you how to check the strings that hang down from the device. Checking your strings regularly can help ensure your IUD is still in place. If you can’t feel the strings or they feel shorter or longer than usual, you should contact your healthcare provider.
- Communicate with Us: If you experience any concerning side effects or have questions about your IUD, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider. They can answer your questions and help you decide whether the side effects you’re experiencing are normal or require further attention.
- Be Patient: While it can be tempting to remove your IUD if you experience side effects, it’s important to be patient and give your body time to adjust. Many side effects, such as cramping and irregular bleeding.
IUD Removal
IUD removal is a simple and straightforward procedure that can be done by a healthcare provider. The removal process is similar to the insertion process and typically takes only a few minutes. Before removal, the healthcare provider will conduct an exam to ensure that the strings attached to the IUD are still visible and in the correct position. The strings are used to gently pull the IUD out of the uterus. Some people may feel slight discomfort or cramping during removal, but this usually lasts only a few seconds.
It’s important to note that IUD removal is recommended when the device has reached the end of its effectiveness or when a person wants to become pregnant or switch to a different form of birth control. Hormonal IUDs usually last between 3-5 years, while non-hormonal copper IUDs can last up to 10 years. If an IUD is left in place beyond its recommended lifespan, it may no longer be effective at preventing pregnancy.
In some cases, people may want to have their IUD birth control Implant removed before it reaches the end of its lifespan due to side effects or personal preferences. Hormonal IUDs can cause hormonal side effects such as mood changes, weight gain, or acne, while copper IUDs can cause increased menstrual bleeding and cramping. If a person experiences these side effects and decides to have their IUD removed, it’s important to discuss alternative birth control options with their healthcare provider.
In rare cases, an IUD may become dislodged or cause complications, such as pelvic pain, fever, or abnormal bleeding. If a person experiences any of these symptoms, they should contact their healthcare provider immediately for evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions About IUD Birth Control
Q: How long does an IUD birth control last?
A: The length of time an IUD lasts depends on the type. Hormonal IUDs can last between 3-7 years, while copper IUDs can last up to 10 years.
Q: Does an IUD hurt when it’s inserted?
A: Some people may experience mild discomfort or cramping during insertion, but it typically only lasts a few minutes.
Q: Can IUDs cause infertility?
A: No, IUDs do not cause infertility. Once an IUD is removed, fertility typically returns to normal.
Q: Can I feel my IUD during sex?
A: It is possible to feel the strings of the IUD during sex, but they should not be uncomfortable or interfere with sexual activity.
Q: Can IUDs be used as emergency contraception?
A: Yes, hormonal IUDs can be used as emergency contraception up to 5 days after unprotected sex.
Q: Can IUDs be used while breastfeeding?
A: Yes, both hormonal and non-hormonal IUDs are safe to use while breastfeeding.
Q: Can IUDs protect against STIs?
A: No, IUDs do not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It’s recommended to use condoms in addition to an IUD to reduce the risk of STIs.
Q: Can IUDs be removed at any time?
A: Yes, an IUD can be removed at any time by a healthcare provider. However, it’s important to use another form of birth control if pregnancy is still desired after removal.
Q: Can IUD birth control be used by everyone?
A: While IUDs are safe for most people, they may not be the best option for everyone. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider to determine if an IUD is a right choice for you based on your individual medical history and preferences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, IUD birth control is a reliable and secure method of birth control that provides a variety of advantages, such as long-term pregnancy prevention, practicality, and reversibility. As with any method of contraception, there may be drawbacks to take into account. To establish if an IUD birth control option is the best for you depending on your unique medical history and choices, it’s crucial to assess the benefits and drawbacks of IUDs and speak with Us. Always keep in mind that there is no one birth control technique that fits all, and what works for one individual may not work for another.
You may make an educated choice about your reproductive health and the most effective birth control technique for you by being aware of the benefits and drawbacks of IUDs.